Numpy Where Functionality
Numpy is a powerful library in Python for performing mathematical operations on arrays and matrices. One useful function in Numpy is numpy.where(), which allows you to perform element-wise conditional operations on arrays.
Syntax of numpy.where()
The syntax for the numpy.where() function is as follows:
numpy.where(condition, [x, y])
Where:
– condition is the condition to be checked
– x is the value to be returned when the condition is True
– y is the value to be returned when the condition is False
Examples of numpy.where()
Here are 10 examples to demonstrate how the numpy.where() function works:
Return elements from two arrays based on a condition
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
arr2 = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
result = np.where(arr1 > 2, arr1, arr2)
print(result)
Output:
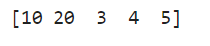
Filter out negative values in an array
arr = np.array([-1, 2, -3, 4, -5])
result = np.where(arr < 0, 0, arr)
print(result)
Output:
[0 2 0 4 0]
Return indices of elements that satisfy a condition
arr = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
result = np.where(arr > 20)
print(result)
Output:
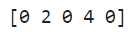
Replace values greater than a threshold with a specific value
arr = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
threshold = 30
result = np.where(arr > threshold, threshold, arr)
print(result)
Output:
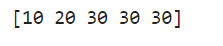
Create a new array based on multiple conditions
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
result = np.where((arr > 2) & (arr < 5), 0, arr)
print(result)
Output:
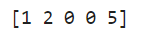
Find the maximum value
arr = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
result = np.max(np.where(arr == np.max(arr)))
print(result)
Output:

Replace NaN values in an array with a specific value
arr = np.array([1, np.nan, 3, 4, np.nan])
result = np.where(np.isnan(arr), 0, arr)
print(result)
Output:
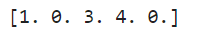
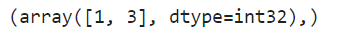
Return indices of non-zero elements in an array
arr = np.array([0, 2, 0, 4, 0])
result = np.where(arr != 0)
print(result)
Output:
Apply different conditions to different elements in an array
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
result = np.where(arr % 2 == 0, -arr, arr)
print(result)
Output:
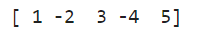
Combine numpy.where() with numpy.sqrt().
arr = np.array([1, 4, 9, 16, 25])
result = np.where(arr >= 10, np.sqrt(arr), arr)
print(result)
Output:
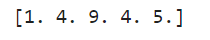
Conclusion of numpy.where()
In conclusion, the numpy.where() function is a versatile tool for performing conditional operations on Numpy arrays. It allows you to efficiently apply different conditions to arrays and create new arrays based on those conditions. Experiment with the examples above to better understand how to leverage the power of numpy.where() in your Python projects.
 NumpyWhere
NumpyWhere